Liver diseases are one of the most common pathologies in the digestive system, with a high incidence. In recent years, the incidence of liver diseases has gradually increased due to obesity, drinking, viral infection and other causes. Liver diseases are not only diverse among individuals, but also highly heterogeneous. At present, the research of liver diseases is mainly conducted through cell culture, animal models, pathological specimens, etc. However, these methods cannot fully reveal the pathogenesis and treatment characteristics of individualized liver diseases.
These issues for disease modeling can be achieved by using organoids containing a variety of organ-specific cell types that self-organize in three dimensions (3D) and exhibit organ-specific structure and function. By mimicking the behavior of diseases in vivo, including the interaction between various cell types, human organoid models can circumvent any species-specific differences in disease pathogenesis and drug response associated with animal models. These properties make them ideal for modeling human diseases.
Liver organoids are functional 3D in vitro models composed of native hepatic cell types. They are widely used as a platform to answer research questions such as liver disease modeling, detoxification and metabolism studies, liver development and regeneration, as well as adult stem cell biology. The liver organoids retain the key physiological characteristics of the liver and are composed of spherical monolayer epithelium.
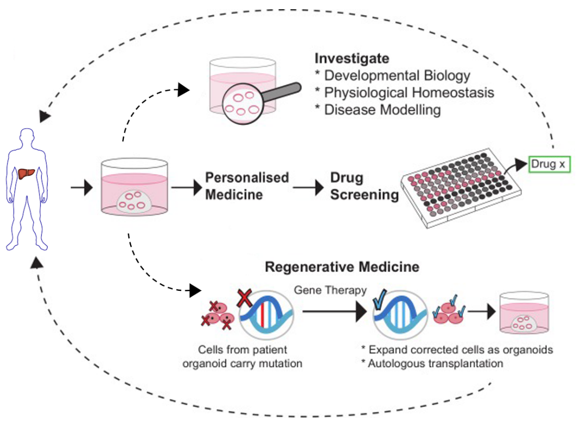
OrganoLab has established liver organoids for multiple species from embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells, hepatoblasts and adult tissue-derived cells. These organoids can help to better understand liver development and regeneration, and provide insights for metabolism research and disease modeling, as well as toxicity assessment and drug screening for personalized medicine. In addition, we can also provide customized in vitro 3D models such as in vitro organoids of specific liver cells, a series of in vitro analysis and screening, with years of experience in organoid technology.
References
- Bin R. et al.; Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Organoids as Models of Liver Disease. Gastroenterology, 2020, 159(4): 1471-1486.
- Hu, Huili et al.; Long-Term Expansion of Functional Mouse and Human Hepatocytes as 3D Organoids. Cell, 2018, 175(6): 1591-1606.
- Mun S. J. et al.; Generation of expandable human pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like liver organoids. J Hepatol. 2019, 71(5): 970-985.
- Wu LJ. et al.; Organoids of liver diseases: From bench to bedside. World J Gastroenterol. 2019, 25(16): 1913-1927.
- Prior N. et al.; Liver organoids: from basic research to therapeutic applications. Gut. 2019, 68(12): 2228-2237.
Online Inquiry
