It is becoming increasingly clear that cancer cell culture models are switching from two-dimension to three-dimension in order to better reflect in vivo situations where tumor cells have to cope with the highly interactive three-dimensional microenvironment. Several such culture models have been reported, mainly multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTS) and patient-derived tumor organoids (PDTO). These are used not only to study the fundamental aspects of cancer development, but also as test systems for innovative therapies against gastric cancer (GC), the fifth most common cancer in the world, and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths. GC exbibits obvious molecular heterogeneity with aggressive behavior and treatment resistance. Therefore, good in vitro models containing unique subtypes are urgently needed for the development precision medicine.
Organoids uniquely mimic tumor initiation and growth, including the steps taken by normal stomach cells to transform into invasive, intestinal-type tumor cells. In addition, they provide sufficient materials for biobanking and screening of novel therapies. Finally, organoids are promising models for personalized treatment and warrant further investigation in drug sensitivity studies for GC patients.
GC organoids are created from fresh surgical or biopsy tissues of a patient's gastric tumor. They are cultured in plastic wells and suspended in a gelatinous matrix, providing a substrate for extension and growth in all dimensions. They grow rapidly and highly represent the molecular landscape, histology and morphology of various subtypes of GC. With respect to the specifics of GC, there are high hopes from such model systems, especially with the aim of identifying prognostic markers and novel drug targets.
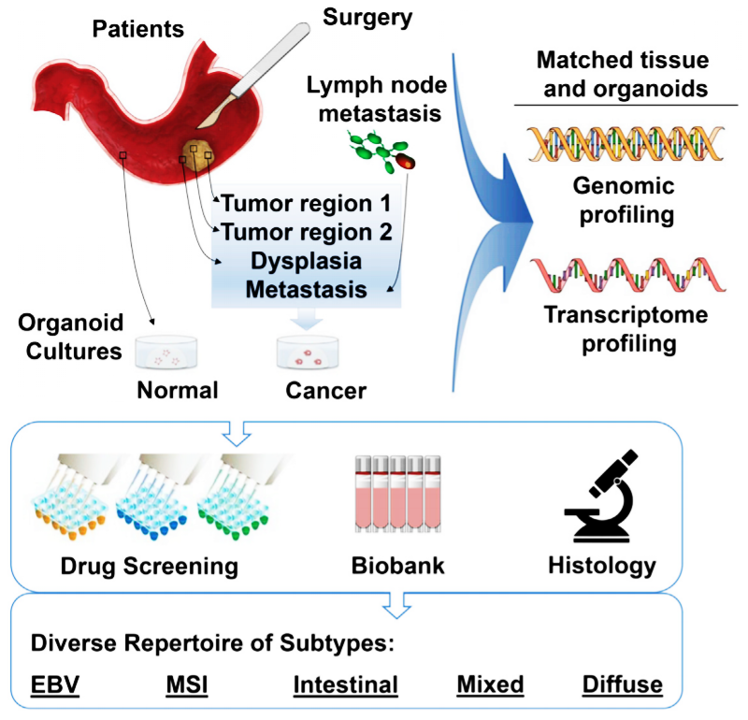 Figure 1. Scheme of gastric cancer organoid culture establishment and performed assays.
Figure 1. Scheme of gastric cancer organoid culture establishment and performed assays.
OrganoLab has established a GC organoid biobank, with comprehensive exome and transcriptome sequencing to decipher their molecular repertoire, as well as to document their stability in long-term culture. Our organoid culture captures early-stage cancers as well as advanced stages, with molecular changes closely matching those of the in vivo frozen tumor samples. With our GC organoids, OrganoLab can provide excellent insights into the basic research of GC and the development of novel therapies. If you have any questions or specific needs, please feel free to contact us.
References
- Alzeeb G. et al.; Three-Dimensional Culture Systems in Gastric Cancer Research. Cancers (Basel), 2020, 12(10): 2800.
- Seidlitz T. et al.; Human gastric cancer modelling using organoids. Gut, 2019, 68: 207-217.
- Yan H. H. N. et al.; A Comprehensive Human Gastric Cancer Organoid Biobank Captures Tumor Subtype Heterogeneity and Enables Therapeutic Screening. Cell Stem Cell. 2018, 23(6): 882-897.
- Lin M. et al.; Utilizing gastric cancer organoids to assess tumor biology and personalize medicine. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019, 11(7): 509-517.
- Steele N. G. et al.; An Organoid-Based Preclinical Model of Human Gastric Cancer. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019, 7(1): 161-184.
- Seidlitz, T. et al.; Gastric organoids—an in vitro model system for the study of gastric development and road to personalized medicine. Cell Death Differ. 2020.
- Thomas, H. Exploring human gastric cancers through organoid culture. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018, 15: 581.
- Steele, Nina G. et al.; An Organoid-Based Preclinical Model of Human Gastric Cancer. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2019, 7(1): 161-184.
Online Inquiry
